Dinasal Dry and Liquid®
Advanced highly efficacious Salmonella inhibition technology
How DINASAL works
Through its unique blend of highly effective active ingredients and surfactants, DINASAL easily penetrates the bacteria cell wall membrane and passes into the cytoplasm. The ensuing bacterial breakdown into anions and cations results in rapid acidification of the cytoplasm which interferes with DNA, RNA, protein synthesis and various other intercellular functions, killing the Salmonella organism.
DINASAL
· Will not interfere with the animals physiology or immune system.
· Will not interfere with vaccination
· programs,
· At 2-5 kg/ton, all naturally occurring salmonella organisms die within 48 hours,
· Kills over 99% of salmonella species in 24 hours,
· Continues to work effectively after 24 hours to help prevent recontamination
· Eliminates salmonella from the finished feed and raw materials.
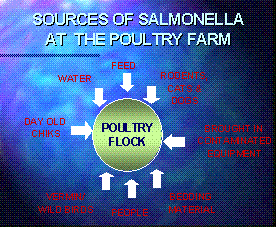
GOOD “HOUSEKEEPING” PRACTICES AGAINST SALMONELLA
The American Feed Industry Association and the Canadian Feed Industry Association have developed guidelines designed to prevent salmonella contamination of feed at the feed manufacturing facility:
. Raw materials and finished feeds must be segregated. This includes having a separate or “dedicated” set of tools, brooms, shovels and handling equipment in each of the areas. Disinfectant foot baths are to be used when personnel move from the raw ingredients to the finished products in the feedmill must be eliminated. Storage bins must be assigned to either pelleted or mash feed.
. Because salmonella requires a moisture content above 10% for growth, all leaks in plumbing must be repaired. Sources of standing water, including leaking roofs and broken windows, must be eliminated. Covers must be properly in place on conveyors.
. Ingredients should be purchased only from reputable suppliers. Ingredients and finished feed should only be transported in dry, clean, and well sealed vehicles.
. Salmonella can be spread by dust, so control of dust by routine cleaning of the feedmill, including overhead pipes and mixing and bagging equipment, will reduce salmonella contamination.
. Trash must be removed frequently. Rodents are many times carriers of salmonella. Disinfectant soap should be provided in employee facilities. Mixing equipment, bins, conveyors and elevator boots should be inspected to eliminate residues and buildup of feed materials and feed.
For state of the art control of salmonella in both feed additives such as meat meal and fish meal and finished feeds. The liquid form consists of USDA approved components. The dry form has the advantage of not having a pungent smell and therefore being more worker/user friendlyThrough its unique blend of highly effective active ingredients and surfactants, DINASAL easily penetrates the bacteria cell wall membrane and passes into the cytoplasm. The ensuing bacterial breakdown into anions and cations results in rapid acidification of the cytoplasm which interferes with DNA, RNA, protein synthesis and various other intercellular functions, killing the Salmonella organism.
DINASAL
· Will not interfere with the animals physiology or immune system.
· Will not interfere with vaccination
· programs,
· At 2-5 kg/ton, all naturally occurring salmonella organisms die within 48 hours,
· Kills over 99% of salmonella species in 24 hours,
· Continues to work effectively after 24 hours to help prevent recontamination
· Eliminates salmonella from the finished feed and raw materials.
GOOD “HOUSEKEEPING” PRACTICES AGAINST SALMONELLA
The American Feed Industry Association and the Canadian Feed Industry Association have developed guidelines designed to prevent salmonella contamination of feed at the feed manufacturing facility:
. Raw materials and finished feeds must be segregated. This includes having a separate or “dedicated” set of tools, brooms, shovels and handling equipment in each of the areas. Disinfectant foot baths are to be used when personnel move from the raw ingredients to the finished products in the feedmill must be eliminated. Storage bins must be assigned to either pelleted or mash feed.
. Because salmonella requires a moisture content above 10% for growth, all leaks in plumbing must be repaired. Sources of standing water, including leaking roofs and broken windows, must be eliminated. Covers must be properly in place on conveyors.
. Ingredients should be purchased only from reputable suppliers. Ingredients and finished feed should only be transported in dry, clean, and well sealed vehicles.
. Salmonella can be spread by dust, so control of dust by routine cleaning of the feedmill, including overhead pipes and mixing and bagging equipment, will reduce salmonella contamination.
. Trash must be removed frequently. Rodents are many times carriers of salmonella. Disinfectant soap should be provided in employee facilities. Mixing equipment, bins, conveyors and elevator boots should be inspected to eliminate residues and buildup of feed materials and feed.
For state of the art control of salmonella in both feed additives such as meat meal and fish meal and finished feeds. The liquid form consists of USDA approved components. The dry form has the advantage of not having a pungent smell and therefore being more worker/user friendly
Salmonella require moisture
Guidelines for moisture control:
- Keep feed materials dry at all times.
- Keep roofs and ceilings leak-proof.
- Construct storage area walls and floors in such a manner as to keep out moisture.
- Avoid or correct conditions conducive to the formation of condensation in
- buildings and equipment. Poorly insulated pipes in the receiving area of the feed mill can result in condensation which will contribute to the spread of bacteria.
- Keep ingredients, finished products, containers, storage areas, and transporting vehicles as dry as possible to prevent growth of Salmonella.
| Sources of Contamination | DINASAL Action |
| Fish meal, offal, meal and bone, Soya, etc. | Immediate kill of contaminating microorganisms and prevention of recontamination |
| Lorries, storage bins, hoppers, augers, etc. | Long-term protection due to the non-volatile nature of the product |
| Contaminated feed, litter, housing, etc. | In-bird effect helps prevent salmonella from infecting bird |
| Food processing areas, cleaning and packaging | Salmonella, Listeria and Campylobacter– free feces will minimize the risk of food |